Quantifying Seismic Activity to Improve Construction Methods
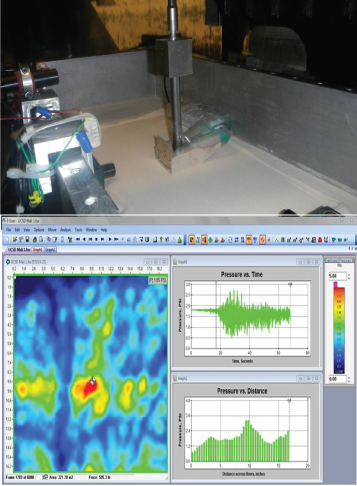 Figure 1: Data from an earthquake simulation study involving a shaker table.
Figure 1: Data from an earthquake simulation study involving a shaker table.
Challenge:
Earthquakes typically occur as a result of natural tectonic activity. Regions of the world that are on the edges of major and minor tectonic plates are thus more likely to experience routine seismic activity that others. As a result, transportation structures that exist in these regions – tunnels, bridges, and overpasses – must be designed to withstand extreme tremors.
Solution:
Pressure mapping was recently used in earthquake lab research studies to determine the environmental impact of earthquakes on certain building materials. In this example, a sensor was mounted on a backfilled vertical wall, a 1:1 scale shaker table to simulate an earthquake. As the test was conducted, the pressure mapping sensor was pressed onto a sample of building material (e.g., a concrete brick, as shown in Figure 1), to record pressure exchanges during the testing duration.
This data gave the researchers better insight into the pressures created by earthquakes, and help builders select stronger materials for transportation structures.
Similar Applications:
- Excavation/drilling applications
- Soil compaction testing
Choose Your Next Destination! Select From the Icons Below
