Joint Analysis
Capture objective & quantifiable data for joint function analysis.
Have questions? Contact Us
Capture objective & quantifiable data for joint function analysis.
The ultra-thin K-Scan™ sensors provide accurate data and quantified analysis of joint function. These ultra-thin sensors are available in various sizes, designs, and configurations for versatility and ease of use.
The system measures pressure, force and contact area between adjacent articulating bones to provide a better understanding of how they are functioning, articulating and loading. There are endless applications for various types of joint research, such as shoulder, wrist, knee, ankle, and more.
|
|
See how researchers at the Cleveland Clinic use K-Scan in their BioRobotics Lab in this video |
See some examples of joint analysis applications in this video |
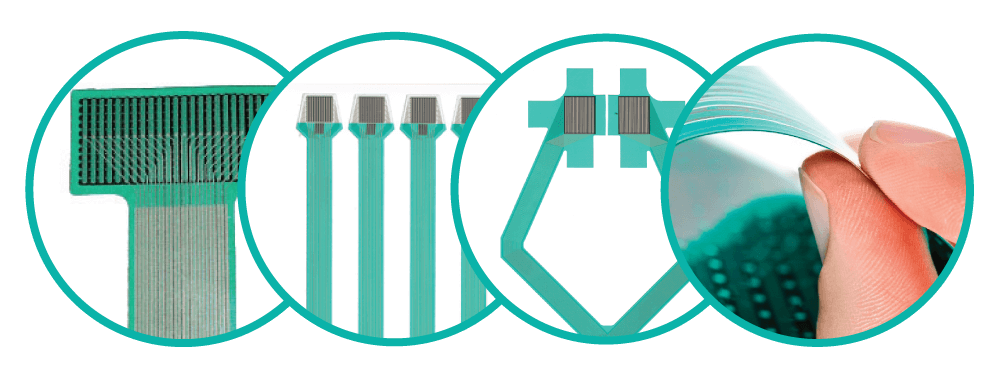
Tekscan's joint analysis system can be found in clinical and research settings worldwide. The system is available with different data connectivity and sensor choices. Learn more about the different K-Scan options and configurations available!
Hover over the icons in the image to see the applicable sensor specifications for each joint.
This free eBook, Joint Function Research Successes with Pressure Mapping, shares several head-to-toe research successes utilizing K-Scan technology.
Researchers & clinicians rely on the accurate and reliable joint contact pressure data from Tekscan for a complete joint analysis.
A recent study published using human cadaveric shoulders stated, 'Tekscan sensors are highly accurate and can collect data points continuously in real time, thereby allowing the fixation techniques to be studied over time.1' Read the full article here.
View the full Joint Analysis Bibliography:
1. Lin, Cheng-Li., et al. (2019) Different suture anchor fixation techniques affect contact properties in humeral greater tuberosity fracture: a biomechanical study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 20:26.